四氯化碳(CCl4)诱导的小鼠肝纤维化和肝硬化是被广泛接受的研究肝纤维化和肝硬化的实验模型。它在许多方面反映了与毒性损伤相关的人类疾病模式,如α-SMA表达、星状细胞活化和关键基质成分(包括胶原蛋白-1、基质金属蛋白酶及其抑制剂TIMPs)已在该模型的发病机制中得到证实。CCl4诱导在肝脏中引起可重现的和可预测的纤维化反应,使其成为抗纤维化和抗肝硬化治疗的临床前药理学研究和肝纤维化-肝硬化-肝癌变化的病理生理学研究的宝贵基础。
四氯化碳诱导的肝纤维化模型建立
实验动物:C57BL/6, 8 weeks old, male
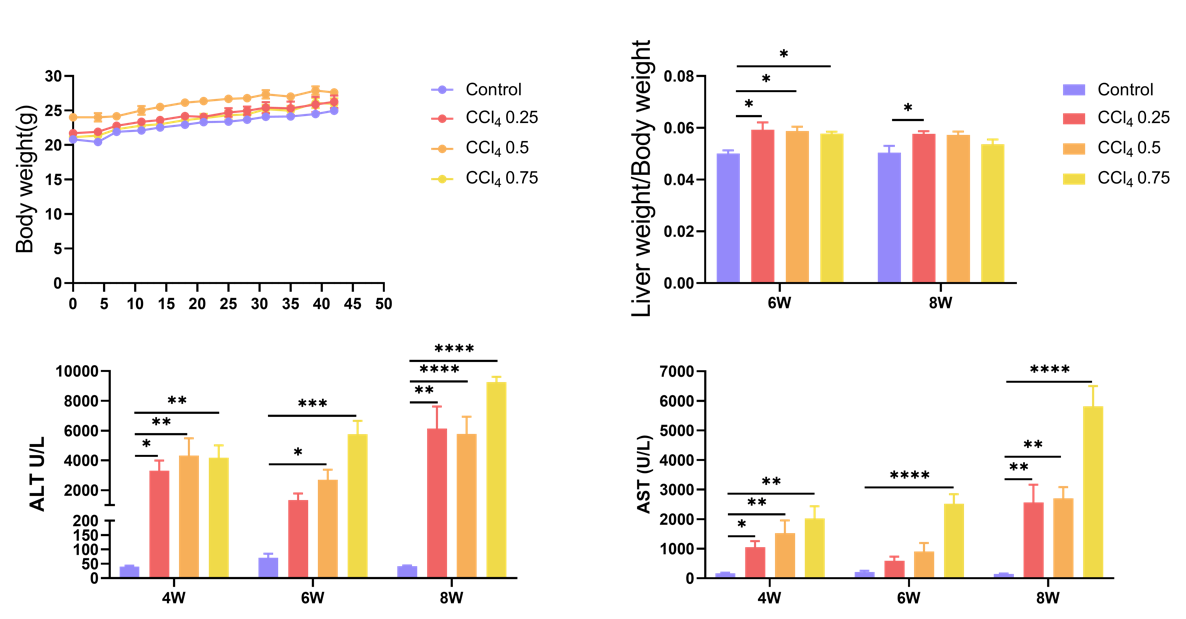
四氯化碳(CCl4)诱导的肝纤维化模型。8周龄雄性C57BL/6小鼠腹腔注射0.25、0.5、0.75 mL/kg CCl4,每周2次。4、6、8周后测定小鼠体质量、肝质量/体质量及血生化指标。
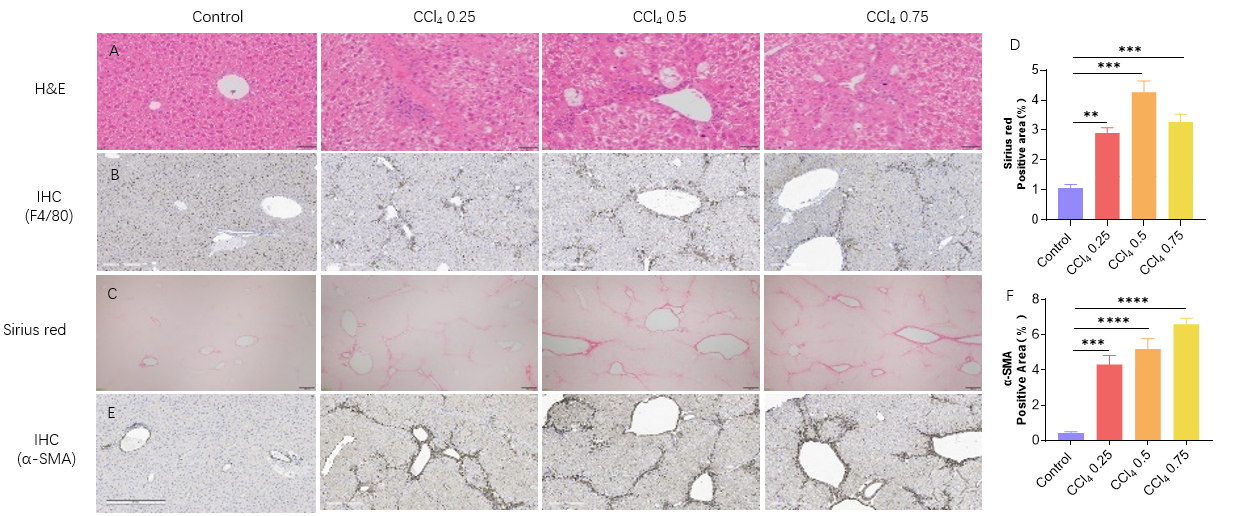
6周CCl4诱导的肝纤维化模型。(A) HE染色显示CCl4诱导后肝脏炎症增加的代表性图片。比例尺:50微米。(B)肝巨噬细胞(枯否细胞)标记物F480的免疫组化代表性图片。(C-D)天狼星红染色显示肝纤维化增加的代表性图片。天狼猩红染色统计数据。比例尺:200微米。(E-F)肝脏成纤维细胞标志物α-SMA免疫组化代表性图片。α-SMA染色统计数据。比例尺:300微米。
奥贝胆酸(OCA)治疗后肝纤维化减少
奥贝胆酸对肝纤维化小鼠模型的药效验证
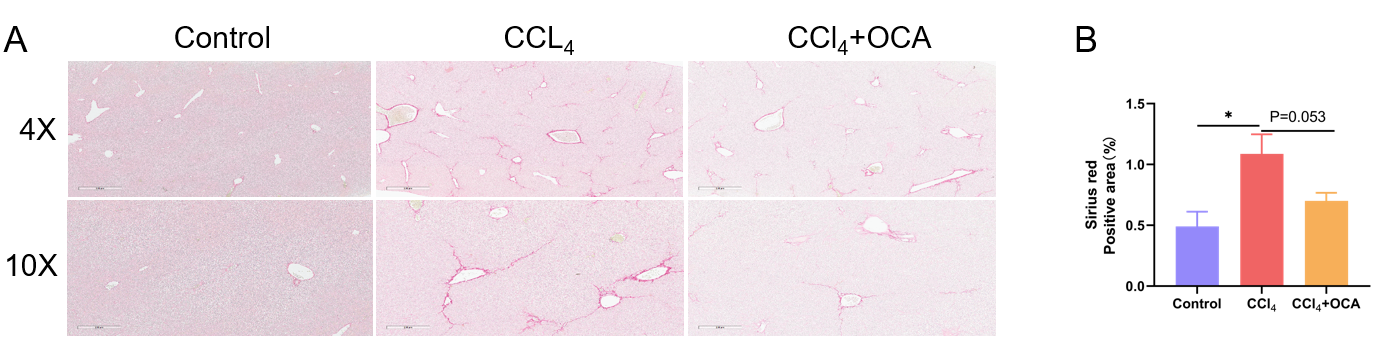
(A)天狼星红染色的代表性图片显示CCl4诱导和OCA治疗3周后的肝纤维化。(B)天狼星红染色的统计数据。数值以平均值±SEM表示。*p<0.05。
参考文献
1. Scholten, D., Trebicka, J., Liedtke, C. & Weiskirchen, R. The carbon tetrachloride model in mice. Lab Anim 49, 4-11 (2015).
2. Hernandez-Perez, E., Leon Garcia, P.E., Lopez-Diazguerrero, N.E., Rivera-Cabrera, F. & Del Angel Benitez, E. Liver steatosis and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: from pathogenesis to therapy. Medwave 16, e6535 (2016).
3. Tsuchida, T., et al. A simple diet- and chemical-induced murine NASH model with rapid progression of steatohepatitis, fibrosis and liver cancer. J Hepatol 69, 385-395 (2018).
4. Farrell, G., et al. Mouse Models of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: Toward Optimization of Their Relevance to Human Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology 69, 2241-2257 (2019).
胆管结扎引起肝外胆道梗阻,导致胆管扩张和胆汁淤积。当胆管内压力进一步升高时,肝内胆管扩张破裂,扩张的胆管和外渗的胆汁共同压迫肝内血管,肝细胞发生缺血坏死,纤维组织增生,包围肝小叶,向肝细胞周围扩散,最终可导致肝硬化。
胆管结扎构建肝纤维化模型
实验动物: C57BL/6, 9 weeks old, male
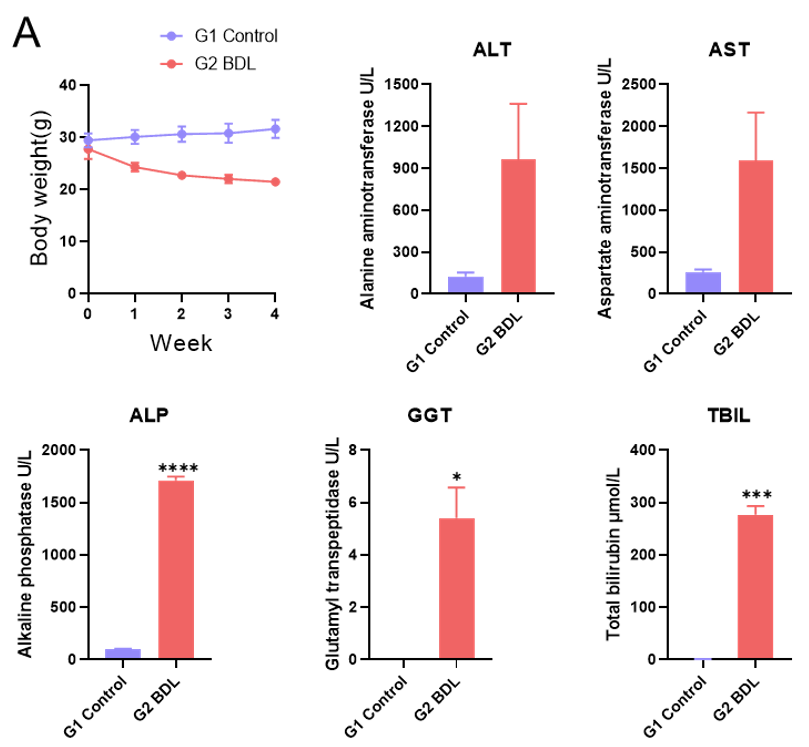
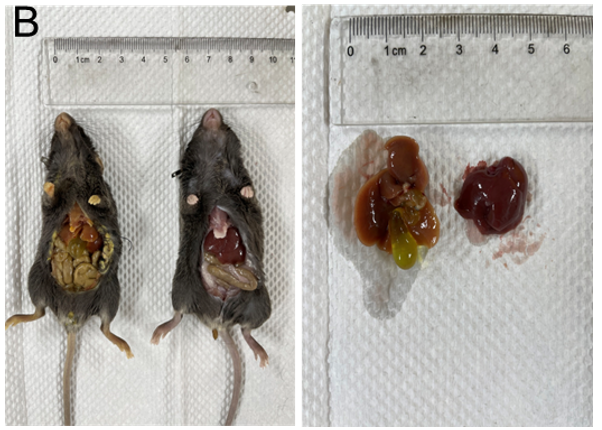
胆管结扎诱导的肝纤维化模型。(A)血清ALT、AST、ALP、GGT、TBIL水平。(B) BDL术后4周肝脏代表性外观。数值以平均值±SEM表示。*p<0.05, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001。
胆管结扎诱导的肝纤维化模型的组织学评估
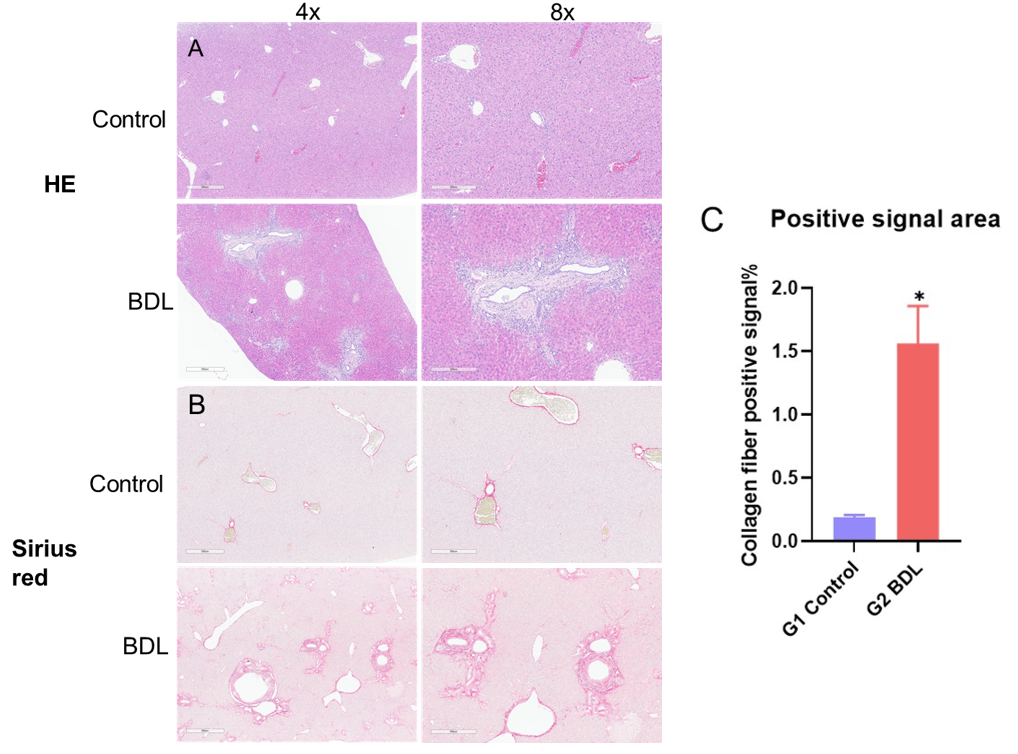
胆管结扎4周后H&E和天狼星红染色。(A) H&E染色的代表性图片。(B)代表性的天狼星红染色显示肝纤维化加重。(C)胶原纤维阳性信号区。数值以平均值±SEM表示。* p < 0.05。
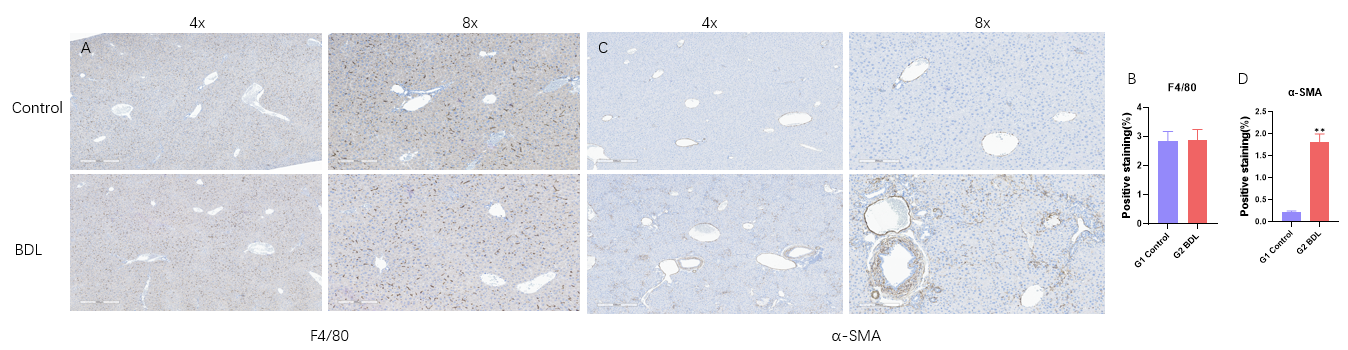
4周后胆管结扎(A-B)免疫组化染色代表性图像显示F4/80及阳性区域。(C-D)免疫组化染色α-SMA及阳性区代表性图像。
硫代乙酰胺(TAA)是一种广泛用于模拟肝纤维化发病过程中产生的损伤的化合物。TAA通过其代谢产物硫代乙酰胺二氧化硫(TASO2)增加活性氧(ROS)的形成,引起严重的氧化应激、脂质过氧化以及蛋白质羰基和DNA加合物的生成。产生的ROS,引起肝星状细胞(HSCs)活化,同时诱导造血干细胞转分化为肌成纤维样细胞,导致EMC合成和降解失衡,持续纤维化过程。
硫乙酰胺肝纤维化模型的建立
实验动物: C57BL/6, 6-8 weeks old, male
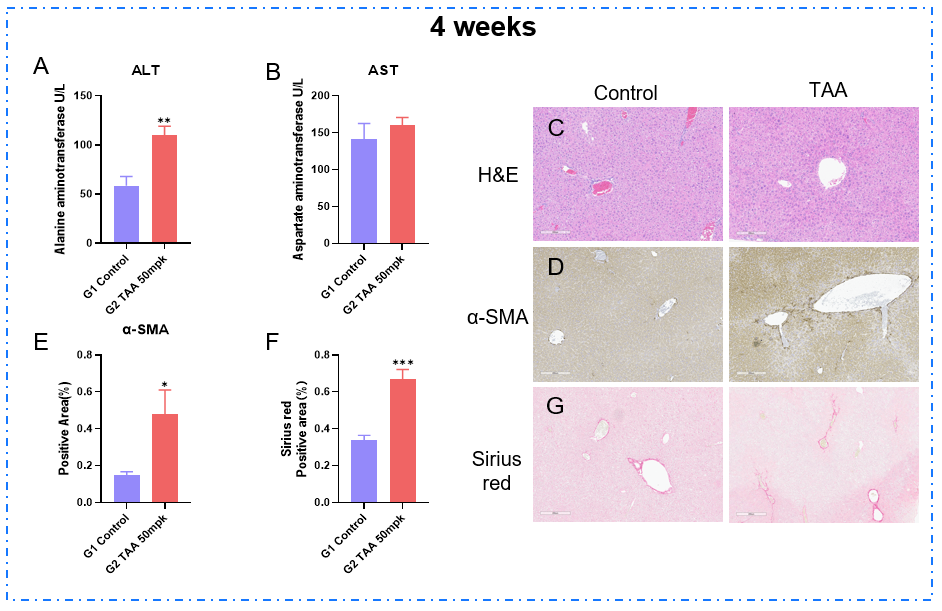
TAA诱导肝纤维化模型4周。(A-B)血清ALT、AST水平。(C) H&E染色代表性图片。(D-E)免疫组织化学染色示α-SMA和阳性区域代表图(G-F)天狼星红染色示肝纤维化增加和阳性区域代表图。
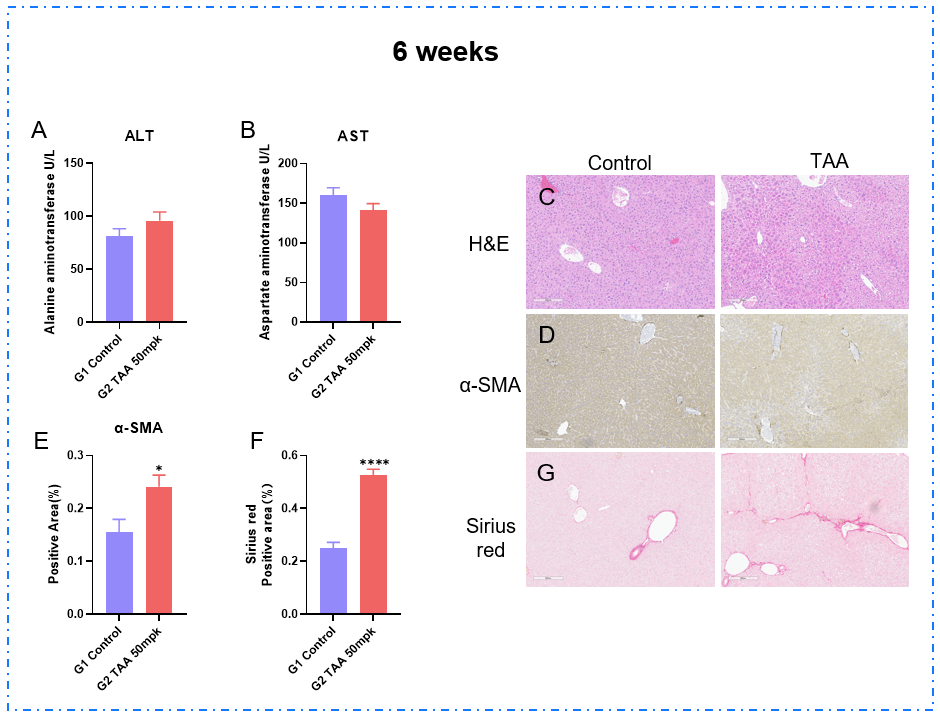
TAA诱导肝纤维化模型6周。(A-B)血清ALT、AST水平。(C) H&E染色代表性图片。(D-E)免疫组化染色α-SMA及阳性区代表图。(F-G)代表性天狼星红染色显示肝纤维化增多和阳性区域。






 010-56967680
010-56967680 info@bbctg.com.cn
info@bbctg.com.cn